The Brief, Mystical Reign of the Wax Cadaver
Early medical models of human anatomy shrouded death in feminine beauty.
BY JOANNA EBENSTEIN
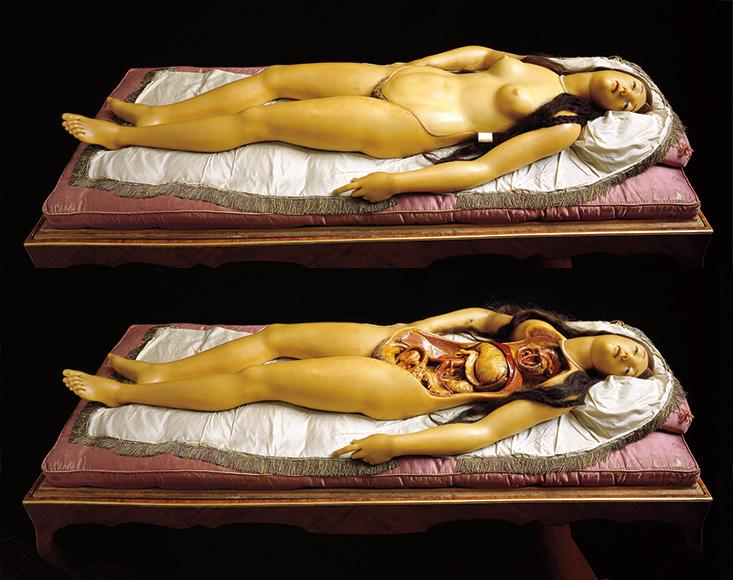 Image courtesy of Museo Della Specola, Florence, Italy / Bridgeman Images
Image courtesy of Museo Della Specola, Florence, Italy / Bridgeman Images
Toward the end of the 18th century, in a wax workshop in Florence, a life-sized, anatomically correct, dissectible goddess of colored wax was created. Artist Clemente Susini took the idealized feminine beauty for which Italian artists had long been renowned in an ambitious new direction, and to hyper-realistic lengths. The result—an Anatomical Venus—is the perfect object: one whose luxuriously bizarre existence challenges belief. It—or better, she—was conceived as a means of teaching human anatomy without the need for constant dissection, which was messy, ethically fraught, and reliant on scarce cadavers. The Anatomical Venus also tacitly communicated the relationship between the human body and a divinely created cosmos, between art and science, and between nature and mankind, as it was then understood.
Often referred to as the “Medici Venus,” this life-sized, dissectible wax woman with gleaming glass eyes and human hair can still be viewed in her original Venetian glass and rosewood case. She can be disassembled into seven anatomically correct layers, revealing at the final remove a tranquil fetus curled in her womb. She and her sisters, wax women in fixed states of anatomical undress sometimes referred to as Slashed Beauties or Dissected Graces, can still be found in a handful of European museums. Supine in their glass boxes, they beckon with a gentle smile or an ecstatic downcast gaze. One idly toys with a plait of real golden human hair; another clutches at the plush, moth-eaten satin cushions of her case as her torso erupts in a spontaneous, bloodless auto-dissection; another is crowned with a golden tiara, while one further wears a silk ribbon tied in a bow around a dangling entrail.
